How The Heart Works
The normal heart is a strong, hardworking pump made of muscle tissue.
It's about the size of a person's fist.
It
pumps blood continuously through the circulatory system. Each day the
average heart "beats" (expands and contracts) 100,000 times and pumps
about 2,000 gallons of blood. In a 70-year lifetime, an average human
heart beats more than 2.5 billion times.
What is the heart's structure?
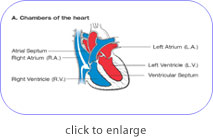
The heart has four chambers through which blood is pumped. The upper two are the right and left atria. The lower two are the right and left ventricles. Four valves open and close to let blood flow in only one direction when the heart beats:
The tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle.
The pulmonary or pulmonic valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
The mitral valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle.
The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Each valve has a set of flaps (also called leaflets or cusps). The mitral valve has two flaps. The others have three. Under normal conditions, the valves let blood flow in just one direction. Blood flow occurs only when there's a difference in pressure across the valves that causes them to open.
How does the heart pump blood?
The heart's four chambers must beat in an organized manner. This is governed by an electrical impulse. A chamber of the heart contracts when an electrical impulse moves across it. Such a signal starts in a small bundle of highly specialized cells in the right atrium -- the sinoatrial node (SA node), also called the sinus node. A discharge from this natural "pacemaker" causes the heart to beat. This pacemaker generates electrical impulses at a given rate, but emotional reactions and hormonal factors can affect its rate of discharge. This lets the heart rate respond to varying demands.