Chemical Engineering Department



Polymers, either synthetic or
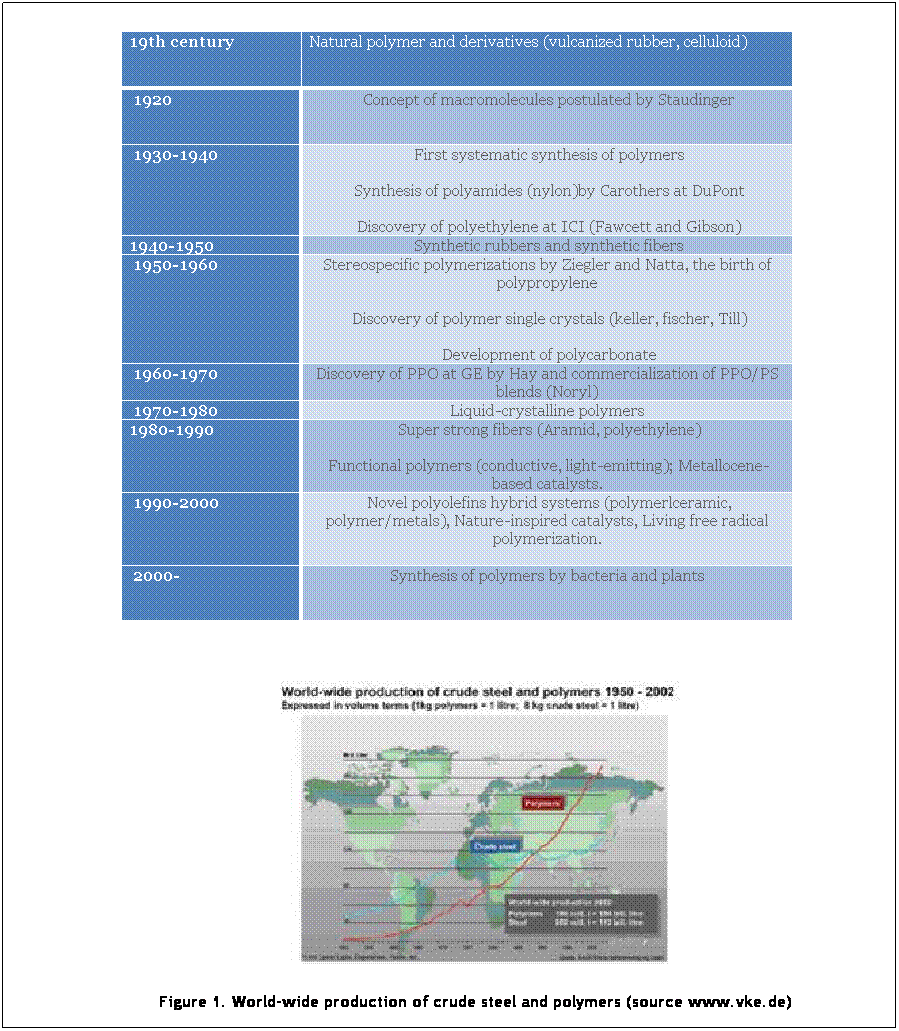
natural, are present in every aspect of our daily lives. Table 1 shows brief
history of polymer development. Many modern functional materials,
pharmaceutical equipments, electronic devices, automobile parts, etc.,
have polymeric components. Polymers are replacing traditional materials
because of their low cost and special applications. Figure 1 shows the
increment of the world-wide production of polymers from 1950 to 2002.
Table 1.
The history of polymers in brief
Dr. Mamdouh A. Al-Harthi,
Associate Professor, Chemical Engineering Department, King Fahd University
of Petroleum & Minerals


Automotive industry Motorists
want high-performing cars combined with reliability, safety, comfort,
competitive pricing, fuel efficiency, and, increasingly, reassurance about
the impact on the environment. Lightweight polymeric materials. Are
increasingly used in this sector (Daimler Benz's Smart is a nice example),
also contributing to a 10% reduction in passenger fuel consumption across
Europe.
Building and construction Polymeric materials are used in the building and
construction sector, for example for insulation, piping, and window frames.
In 2002 this sector accounted for 17.6% of the total polymer consumption.
Electrical and electronic industry Many applications in this field arise
from newly designed polymeric materials, for example for polymeric solar
cells and holographic films. It is interesting to note that, while the
number of applications in this field is increasing, the weight of the
polymers used per unit is decreasing.
Packaging The packaging sector remains the largest consumer of synthetic
polymers, approximately 38% of the total market. This is mainly due to. the
fact that these materials are lightweight, flexible, and easy to process,
and are therefore increasingly being substituted for other materials.
Although polymer packaging ranks first in terms of units sold, it is only
third if judged on weight.
Agriculture As agricultural applications account for about 2.5% of the total
of synthetic polymers consumed in Europe, they play only a marginal role.
Irrigation and drainage systems provide effective solutions to crop growing,
and polymeric films and greenhouses can increase horticultural production
substantially. The use of so called "super absorbers" for increased
irrigation efficiency in arid areas can be considered an important emerging
market.
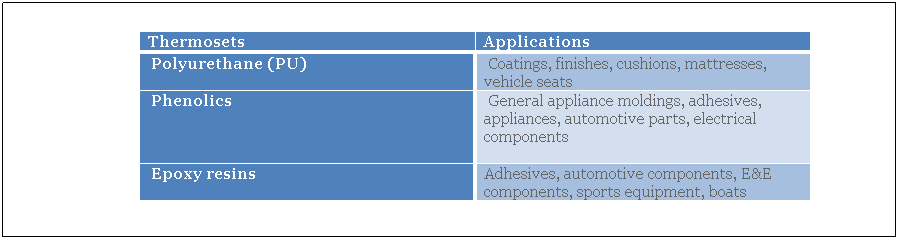
Tables 2 and 3 present some polymers with their applications.
Table. 2. Applications for the major thermoplastics [2].
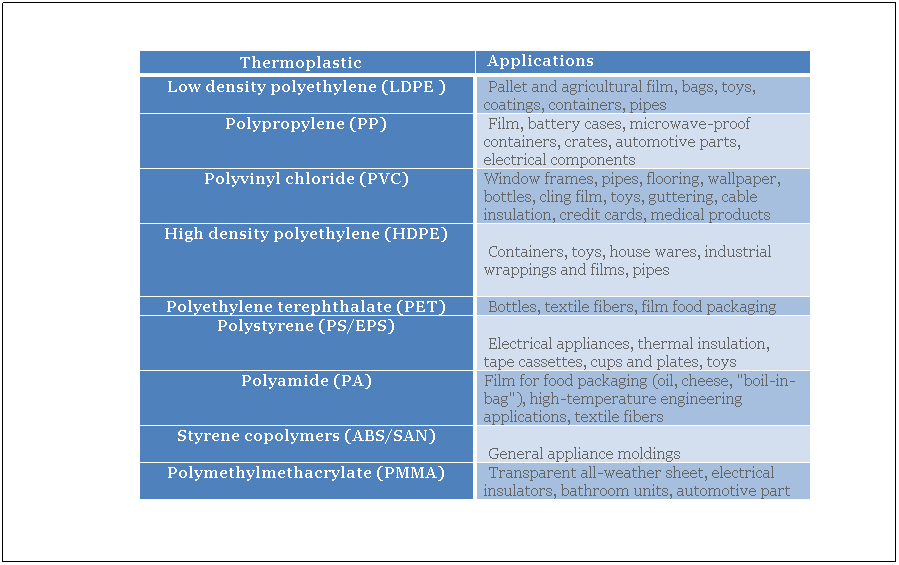
Table. 3. Applications for the major thermosets [2].
The development of new
polymers and the modification and enhancement of the old ones are goals of
many researchers in both industry and academia. A breadth of knowledge has
been built over the years which involve aspects of organic chemistry,
physical chemistry, analytical chemistry, physics, chemical and mechanical
engineering. Those sciences are integrated to support the in-depth analysis
of polymer synthesis, structure, kinetics, characterization, and processing
in order to relate to the performance of the polymer in end use. If polymer
chains are completely characterized and the structural basis of its
properties are known, the polymerization reaction can be optimized and
controlled to produce the optimum properties from a particular chemical
system.
[1] Handbook of polymer reaction engineering (2005)
[2] Association of Plastics Manufacturers in Europe. (2002)





